What is business intelligence?
Business intelligence (BI) uncovers insights for making strategic decisions. Business intelligence tools analyze historical and current data and present findings in intuitive visual formats.
How business intelligence works
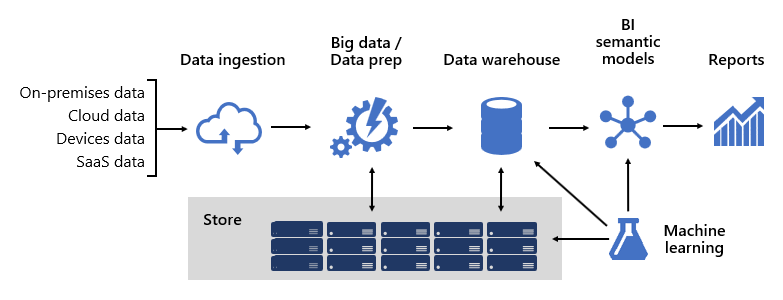
There are four keys steps that business intelligence follows to transform raw data into easy-to-digest insights for everyone in the organization to use. The first three—data collection, analysis, and visualization—set the stage for the final decision-making step. Before using BI, businesses had to do much of their analysis manually, but BI tools automate many of the processes and save companies time and effort.
Step 1: Collect and transform data from multiple sources
Business intelligence tools typically use the extract, transform, and load (ETL) method to aggregate structured and unstructured data from multiple sources. This data is then transformed and remodeled before being stored in a central location, so applications can easily analyze and query it as one comprehensive data set.
Step 2: Uncover trends and inconsistencies
Data mining, or data discovery, typically uses automation to quickly analyze data to find patterns and outliers which provide insight into the current state of business. BI tools often feature several types of data modeling and analytics—including exploratory, descriptive, statistical, and predictive—that further explore data, predict trends, and make recommendations.
Step 3: Use data visualization to present findings
Business intelligence reporting uses data visualizations to make findings easier to understand and share. Reporting methods include interactive data dashboards, charts, graphs, and maps that help users see what’s going on in the business right now.
Step 4: Take action on insights in real time
Viewing current and historical data in context with business activities gives companies the ability to quickly move from insights to action. Business intelligence enables real time adjustments and long-term strategic changes that eliminate inefficiencies, adapt to market shifts, correct supply problems, and solve customer issues.
Why companies benefit from using business intelligence tools
Because business intelligence tools speed up information analysis and performance evaluation, they’re valuable in helping companies reduce inefficiencies, flag potential problems, find new revenue streams, and identify areas of future growth.
Some of the specific benefits that businesses experience when using BI include:
- Increased efficiency of operational processes.
- Insight into customer behavior and shopping patterns.
- Accurate tracking of sales, marketing, and financial performance.
- Clear benchmarks based on historical and current data.
- Instant alerts about data anomalies and customer issues.
- Analyses that can be shared in real-time across departments.
In the past, business intelligence tools were primarily used by data analysts and IT users. Now, self-service BI platforms make business intelligence available to everyone from executives to operations teams.
Microsoft BI Ecosystem
The eco systems can be divided into four separate layers. 1. ETL Layer 2. Warehouse Layer 3. OLAP Layer 4. Reporting Layer Let me explain these layers in a little more detail.
1. ETL Layer
This is the layer which extracts the data from the LOB systems in the organization like the ERP, CRM, SAP, Oracle Fusion, Dynamics, and Salesforce etc. and transforms the data by applying business rules if any and loading the data into the data warehouse and the SQL Component which covers this is called SQL Server Integration Services.
2. Warehouse Layer
This is the layer where we store data in a dimensional mode, which means data is split into dimensions and fact tables (Star or Snowflake schema based on business rules). The SQL Component which covers this is called SQL Relational Database Engine.
3. OLAP Layer
This is the analytics layer which pre-aggregates the data and stores it for faster fetching of data. The SQL component which covers this are called SQL Server Analysis Services and comes in two modes a Tabular Model which is an In Memory module with data loaded in Memory for faster access and the other is a multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP) model where the data is stored in disk.
4. Reporting Layer
The Reporting layer which consists of components like Power BI, Data Zen, SQL Server Reporting Services, PowerPivot\View on Excel can directly read from the source systems.
When do I get what and how will I get charged for is a question which comes to our mind. There are two main components to be bought.
SQL Server
SQL Server has a core based licensing and let us say we buy 16 Cores of SQL License. I can install this on a single box with all the SQL components which are mentioned above.
i. SQL Database Relational Engine.
ii. SQL Server Integration Services
iii. SQL Server Analysis Services.
iv. SQL Server Reporting Services
v. Datazen for SQL 2014 and below (It is integrated into SQL Server Reporting Services from 2016 onwards )There is no additional licensing for each component, when you buy SQL Server License, you have the entire stack at your disposal.Another alternative to it could be to deploy couple of components on one server with 8 crores. Let us say the relational database engine, Integration Services are on Server A, SQL Server Analysis Services and Reporting Services on another server, let us call it Server B which has 8 cores which is typically called the scale out architecture in case of intensive ETL and Reporting requirements.
It is also possible that ETL workload is so huge when in Terabytes that 16 Cores is utilized by one server with the relational database engine and you will need to additionally buy more SQL Server Core Licenses for other components such as SSIS, SSAS, SSRS.
Power BI
Power BI is a cloud based service which is more used for Self Service BI with powerful features such as Natural Language Query which can get data from various different sources like Oracle, SAP BW, SAP Hana, Facebook etc.. It has got its own Desktop component which is free. The data refresh can be scheduled using the Enterprise Gateway component or the personal gateway. The Licensing is user based and you can buy this as an Individual component or bundled with 0365 upward of E4 License.Now the question arises if I have Power BI which can connect to any source why do I need SQL Server? The answer is that when you connect to the core systems all the data might not reside in one system and also when you query the data for multiple months etc. It might impact the performance of the core system. This could also lead into data retrieval not being fast enough if the underlying database is modeled as a transaction database instead of a dimensional model which is meant for reporting.
Also if you need features where a person from a specific region should be able to access data pertaining to their region only then you will need to have a DWH with SSAS involved.
https://powerbi.microsoft.com/en-us/what-is-business-intelligence/
